AMB 102 Practical Hand Book Assignment Question and Answers



The above image is our AMB practical assignment, solve the marked Numbers submit on or before Wednesday next.
ANSWERS
1. Define microscope and microscopy
- Microscope: A microscope is an optical or electronic instrument that magnifies small objects, making them visible to the human eye. It allows scientists and students to study structures and details of organisms, cells, and materials that cannot be seen unaided. Microscopes can be simple (one lens), compound (multiple lenses), or advanced (like electron microscopes) depending on their design and purpose.
- Microscopy: Microscopy is the branch of science and technique that deals with the use of microscopes for investigating small objects and fine details. It involves methods of preparing specimens, focusing, magnifying, and interpreting what is seen under the microscope. Microscopy has wide applications in biology, medicine, chemistry, and materials science.
3. What major components are required to make a local light microscope? Please be detailed to your specifications.
The major components required to make a local light microscope are:
- Eyepiece (ocular lens): This is the lens at the top where I look through. It usually gives a magnification of about 5x to 15x.
- Objective lenses: These are the main lenses close to the specimen, fixed on a rotating nosepiece. They give different levels of magnification such as 4x, 10x, 40x, and sometimes 100x.
- Stage: This is the flat platform where the glass slide holding the specimen is placed. It often has clips to hold the slide in position.
- Light source (illuminator): This provides the light that passes through the specimen. In local microscopes, it can be a small lamp, a mirror, or even natural light.
- Condenser lens: This lens focuses the light onto the specimen so that the image is clearer. It may also have a diaphragm to control how much light passes through.
- Body tube (or head): This part connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses and keeps the optics in proper alignment.
- Arm (or frame): The arm supports the main parts of the microscope and also serves as a handle for carrying it.
- Coarse adjustment knob: This knob is used to move the stage up and down for rough focusing of the specimen.
- Fine adjustment knob: This knob helps to sharpen the image after using the coarse knob, giving a clearer and more precise view.
- Base: This is the bottom part that supports the whole microscope. In some models, the light source is also housed in the base.
4. X-ray the basic components of a microscope.
The basic components of a microscope include the eyepiece for viewing, the objective lenses for magnification, the stage for holding the specimen, a light source or mirror for illumination, a condenser to focus light, the arm and base for support, and the coarse and fine adjustment knobs for focusing.
page 12
1. Draw and label five different equipment and instrument, in the Microbiology Laboratory
- Microscopes (Compound and Stereo)
- Autoclaves
- Incubators
- Biosafety Cabinets
- Centrifuges
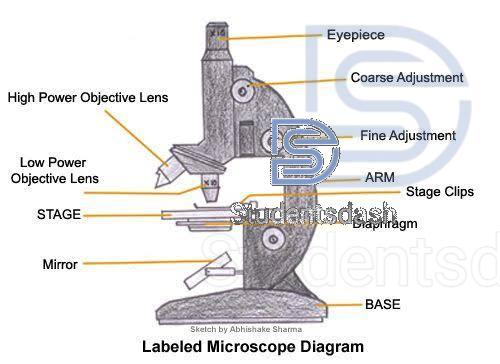
Microscopes (Compound and Stereo)
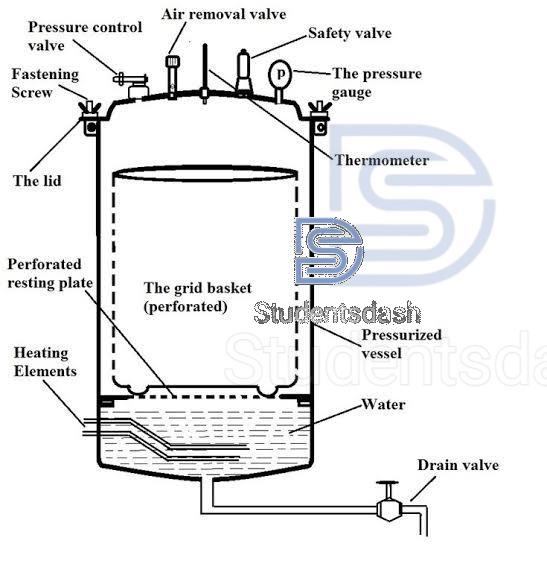
Autoclaves
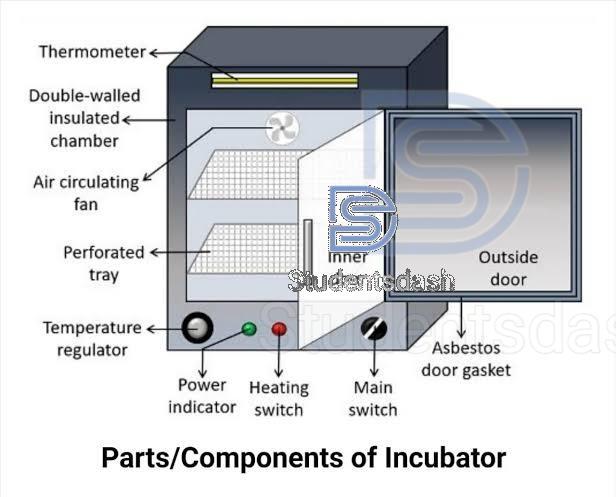
Incubators
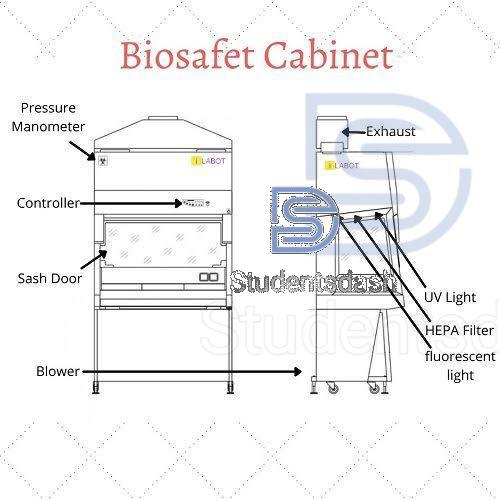
Biosafety Cabinets
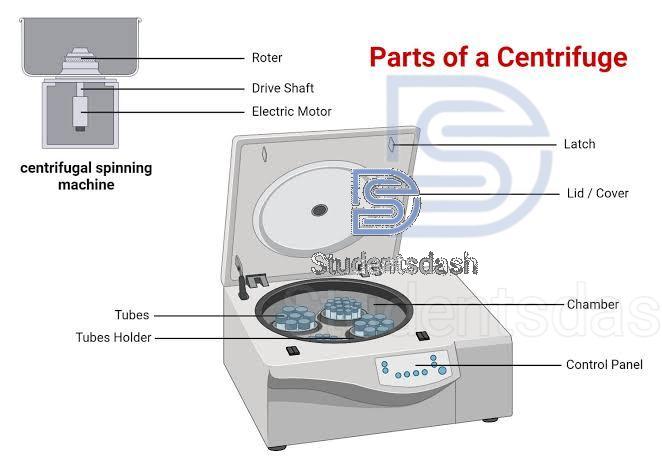
Centrifuges
3) Draw and label binocular microscope (ii) State the functions of the labeled parts
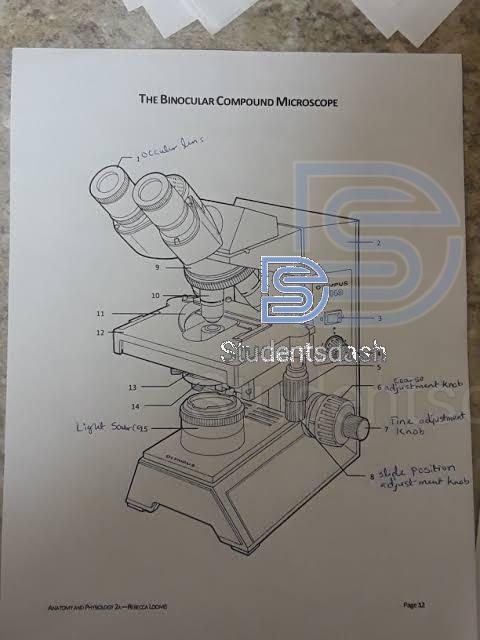
ii) Functions of the labeled parts
- Ocular lens (eyepiece): Used to view the specimen. It further magnifies the image formed by the objective lens.
- Body tube / Head: Holds the eyepiece and connects it to the objective lenses, keeping everything aligned.
- Revolving nosepiece (turret): Holds the objective lenses and allows the user to switch between them.
- Objective lenses: Provide the main magnification (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x).
- Stage clips / slide holder: Keep the specimen slide firmly in place on the stage.
- Stage: A flat platform where the specimen slide is placed for observation.
- Coarse adjustment knob: Moves the stage up and down quickly to bring the specimen into general focus.
- Fine adjustment knob: Moves the stage slightly to sharpen the focus and give a clearer image.
- Light source (illuminator): Provides the light needed to pass through the specimen for visibility.
- Condenser lens: Focuses light onto the specimen to improve clarity and contrast.
- Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that passes through the specimen.
- Arm: Supports the microscope’s body and is used for carrying the instrument.
- Base: The bottom part of the microscope; it provides support and stability, and sometimes houses the light source.
- Stage position adjustment knobs (mechanical stage controls): Move the slide horizontally (left–right, forward–backward) to position the specimen under the objective lens.
4. The standard temperature and pressure for sterilization in an autoclave is 121 °C and 15 psi (pounds per square inch).
5. List two laboratory instruments that cannot be sterilized with the use of autoclave.
Two laboratory instruments that cannot be sterilized using an autoclave are:
1. Plastic or rubber materials (that melt or deform under high heat and pressure).
2. Powders, oils, or oily preparations (since moisture and high pressure damage them).
6. Mention four glass wares commonly used in the microbiological laboratory.
Four glasswares commonly used in the microbiological laboratory are:
- Test tubes
- Petri dishes
- Beakers
- Conical flasks (Erlenmeyer flasks)
❤️
for more sch guides and news download studentsdash app or join our WhatsApp group

