Let’s go through the questions step by step:
Question 1: Compute for SS, DF, MS, and F-ratios using the AB Sum Matrix table.



Question 2: Verifying the relationship between tribe and party affiliation using Chi-square.
We are asked to check whether there is a significant relationship between tribe and party affiliation at a 0.01 level of significance using the critical value of 13.28.
Steps:
1; Set up a hypothesis:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no relationship between tribe and party affiliation.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a relationship between tribe and party affiliation.
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no relationship between tribe and party affiliation.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a relationship between tribe and party affiliation.
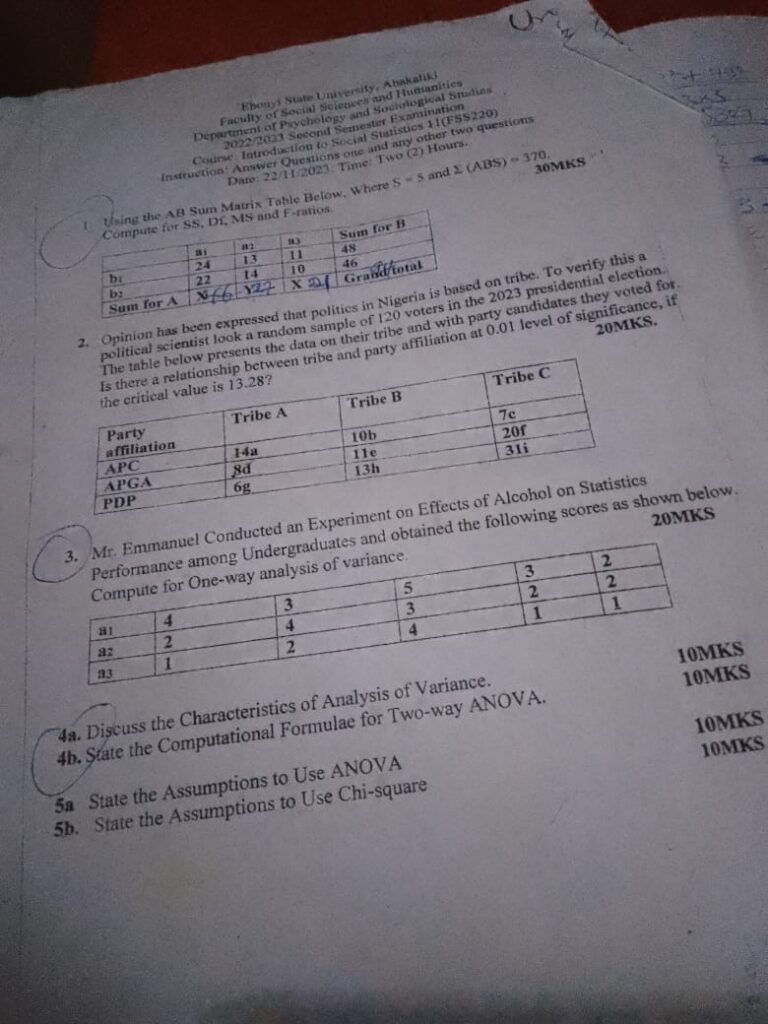
- Compute the Expected Values:
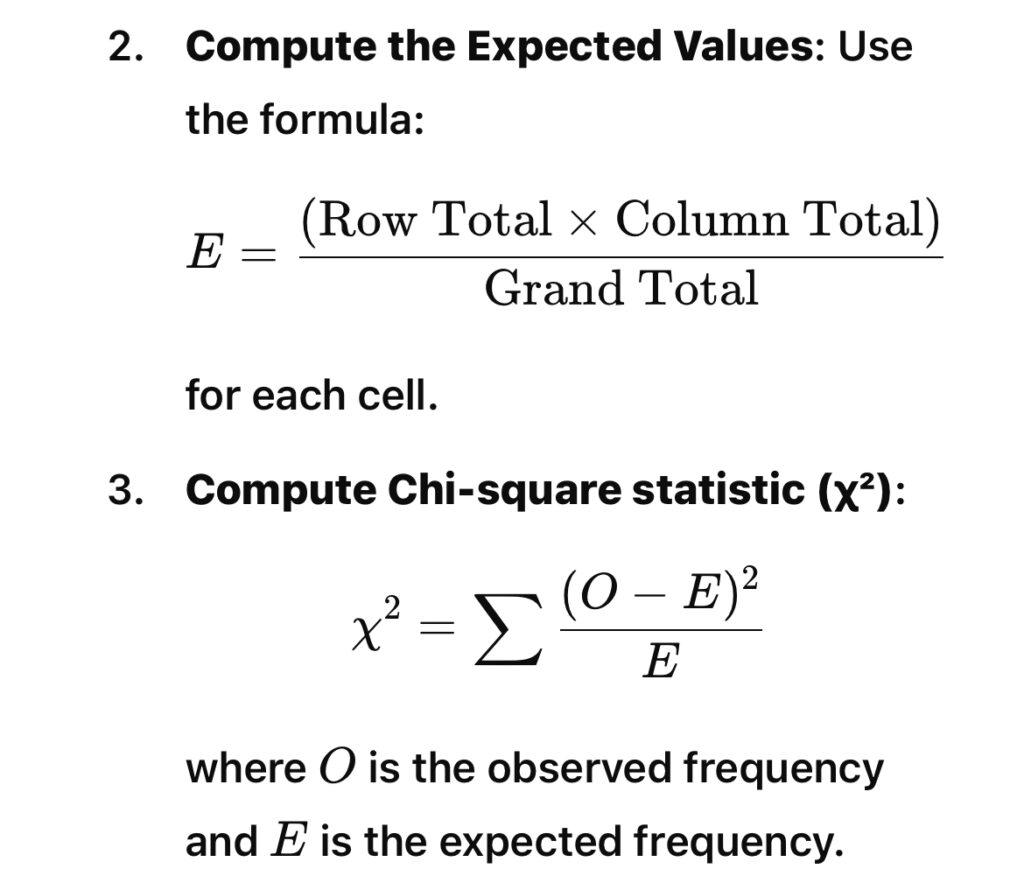
4. Compare χ² value:
If the calculated chi-square statistic is greater than the critical value of 13.28, we reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, we fail to reject it.
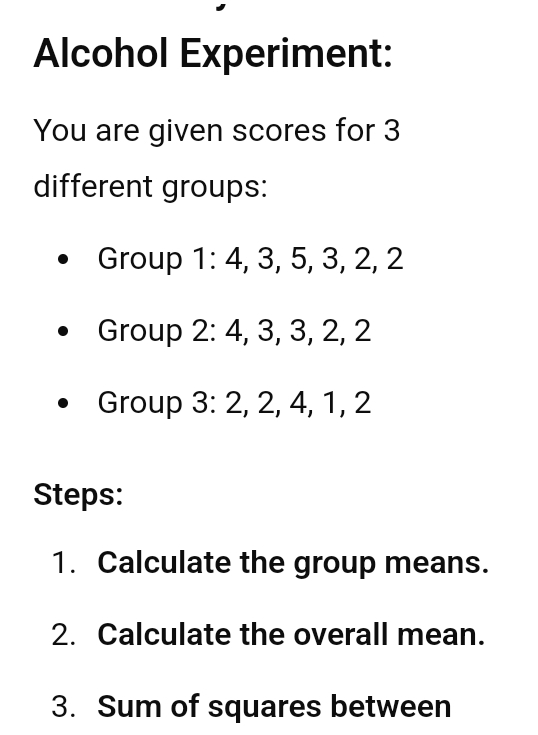
Question 3: Compute for One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).
We have been given a table of scores to compute a one-way ANOVA.


Question 4a: Discuss the Characteristics of Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).
Characteristics of ANOVA:
- Comparison of Multiple Groups: ANOVA is used to compare the means of three or more independent groups.
- Variance Partitioning: ANOVA partitions total variance into between-group variance and within-group variance.
- Hypothesis Testing: It tests the null hypothesis that the group means are equal.
- F-ratio: ANOVA produces an F-ratio, which is the ratio of between-group variance to within-group variance.
- Assumptions: ANOVA assumes normal distribution, independence of observations, and homogeneity of variance.
- Post-hoc Tests: If significant differences are found, post-hoc tests are used to determine which groups differ.
- Factorial ANOVA: ANOVA can be extended to more than one independent variable in factorial designs.
- Sensitivity: It is sensitive to the sample size and variance differences among groups.
- Data Requirements: ANOVA requires continuous dependent variables and categorical independent variables.
- Non-parametric Alternatives: If assumptions are violated, non-parametric tests like Kruskal-Wallis can be used.
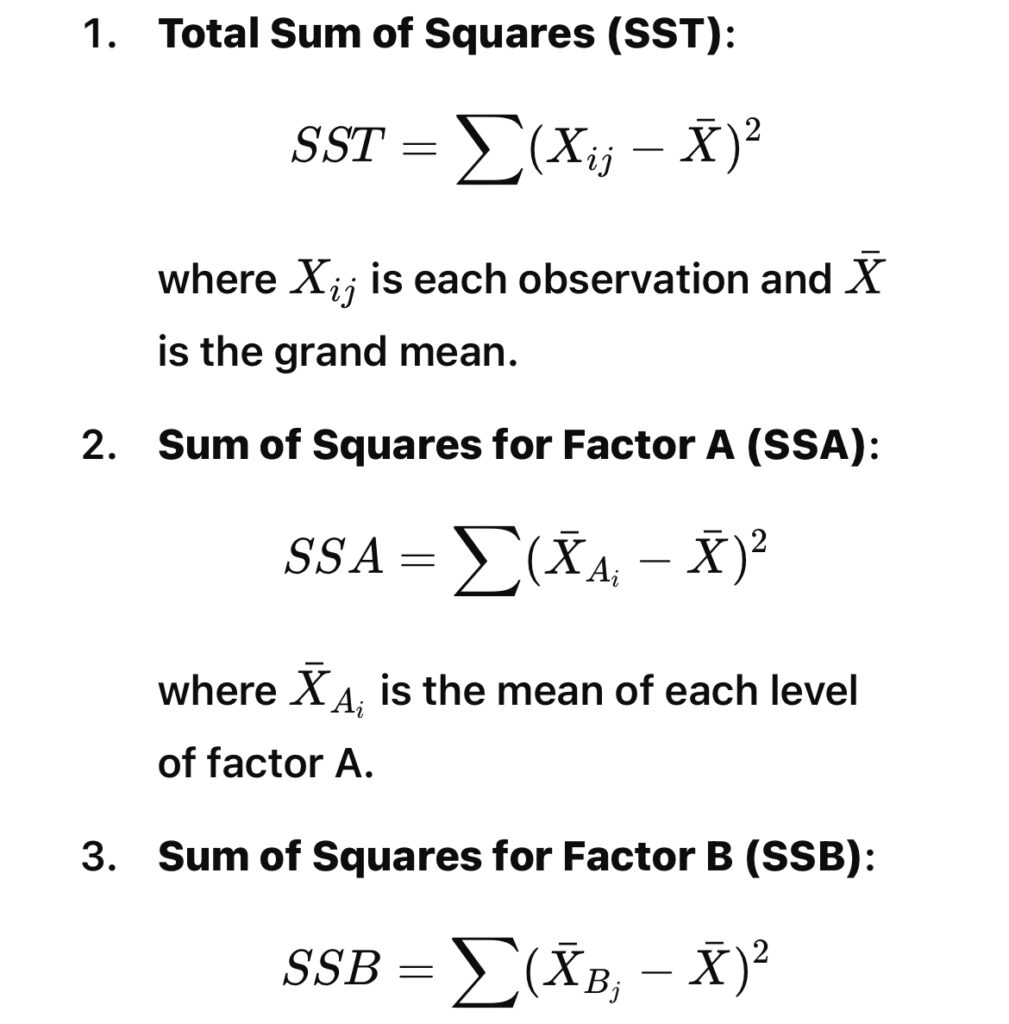
Question 4b: State the Computational Formulae for Two-way ANOVA.
The two-way ANOVA involves two factors. The formulae are:
Question 5a: State the Assumptions to Use ANOVA.
- Independence of Observations: The data for each group should be independent.
- Normal Distribution: The data within each group should follow a normal distribution.
- Homogeneity of Variance: The variance among the groups should be approximately equal.
- Random Sampling: The samples should be randomly selected from the population.
- Continuous Data: The dependent variable should be measured on a continuous scale.
Question 5b: State the Assumptions to Use Chi-square.
- Independence: The observations must be independent of each other.
- Categorical Data: The data must be in the form of counts for categories.
- Expected Frequency: Each expected frequency in a contingency table should be 5 or more.
- Random Sampling: The data should be obtained from a random sample.
- Adequate Sample Size: The sample size should be large enough to ensure the accuracy of the test.
Nice one keep up the good work 👍👏